
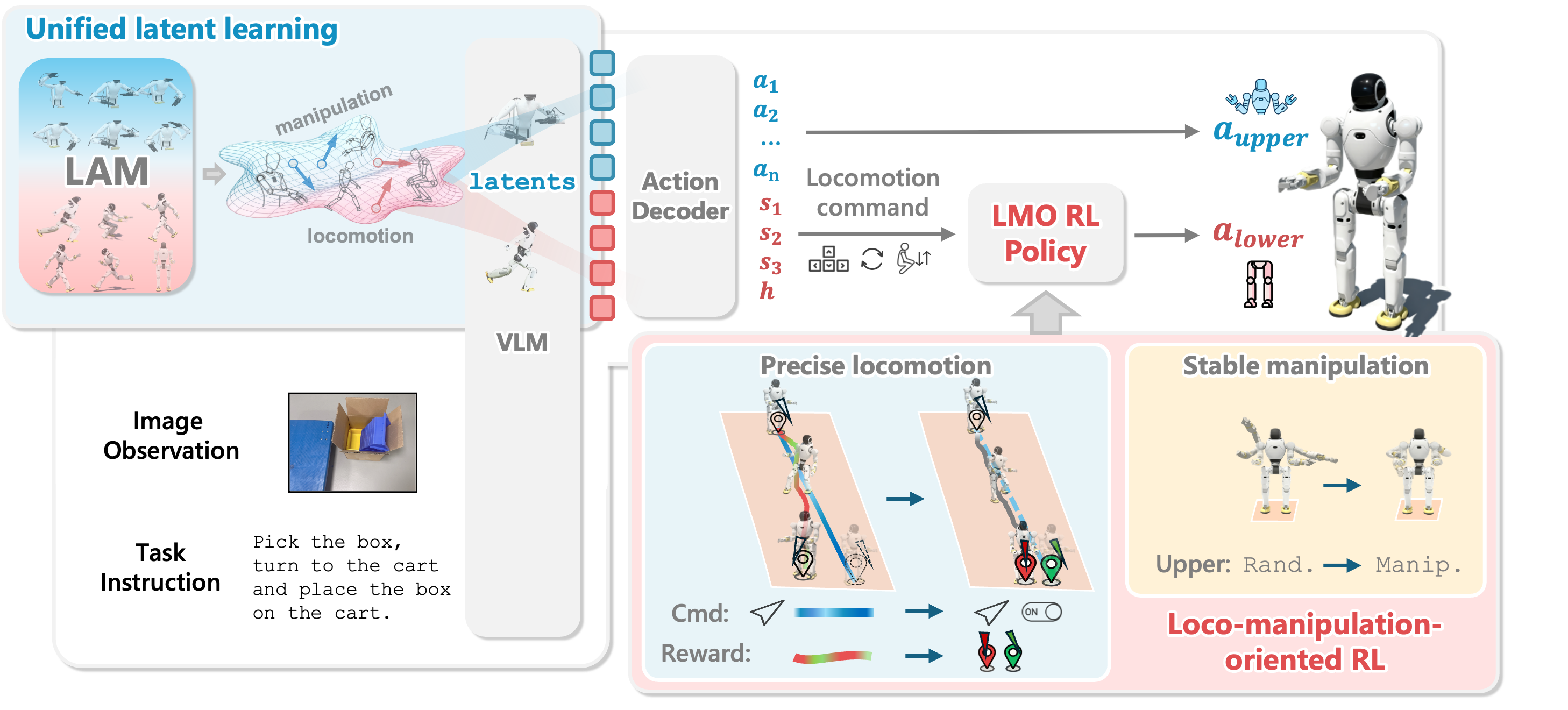
WholeBodyVLA Performance in Complex Tasks
Adaptability & Scalability
Demonstrate WholeBodyVLA's robustness to variations in objects appearance and position, layout, and table color, in response to Reviewer C1fR (W2 Q2 S2) and Reviewer 76f3 (W1).
Showcase WholeBodyVLA's ability to compose forward advancing, sidestepping, turning, and squatting to handle diverse start-poses (X/Y offsets, orientations, and table heights), in response to Reviewer C1fR (W2 Q2 S2) and Reviewer N1iB (W1 Q1).
Demonstrate WholeBodyVLA's ability to traverse uneven terrain, in response to Reviewer C1fR (W2 Q2 S2), Reviewer N1iB (Q4), and Reviewer 1asV (W2).
Demonstrate WholeBodyVLA's competence on long-horizon sequences that involve loco-manipualtion and whole-body coordinated actions, in response to Reviewer C1fR (W2 Q2 S2), Reviewer N1iB (Q4), and Reviewer 1asV (W2 W3).
Showcase WholeBodyVLA's scalability to more complex everyday loco-manipulation tasks (e.g., wiping, vacuum cleaning, etc), in response to Reviewer C1fR (W2 Q2 S2), Reviewer N1iB (Q4), Reviewer 76f3 (W1 W2), and Reviewer 1asV (W2).